What is oral cancer?
Oral cancer is a malignant tumor that starts in the mouth. It may occur in the lips, gum, tongue, palate, jaw bone, floor of the mouth, oral pharynx, salivary glands, maxillary sinus and mucous membrane of the facial skin.
What is the incidence of oral cancer?
The incidence of oral cancer accounts for 1.45% to 5.6% of all the malignant cancers with a higher percentage among males than females.
What are the causes of oral cancer?
Long-term addiction to smoking or drinking: most oral cancer patients have long history of smoking or drinking. Non-smokers and Non-drinkers are seldom found with oral cancer.
Bad oral hygiene: bad oral hygiene provides a nourishing environment for the growth and multiplication of bacteria and mycetes, which are beneficial to the formation of nitrosamine.
Long-term stimulation of foreign body: long-term stimulation to the mucous membrane of the oral cavity by root of teeth, sharp teeth cusps or unsuitable false teeth, can cause chronic ulcer and cancerous lesion.
Innutrition: lack of elements like vitamin A1, vitamin B2 and trace element zinc, arsenic, can raise the organism’s sensitivity to carcinogen and causes oral cancer.
Leukoplakia and erythroplakia: oral leukoplakia and proliferative erythroplakia are signs of cancerous lesion.
Ultraviolet rays: for outdoor workers, long-term exposure to direct sunlight can raise the risk of oral cancer.
Ionizing radiation: ionizing radiation can cause changes of DNA and activate the cancer genes, thus, causes cancer.
Others: diseases like chronic hepatitis, cirrhosis and virus infection, which can cause decrease of the organism’s immunity, also have relation to the incidence of oral cancer.
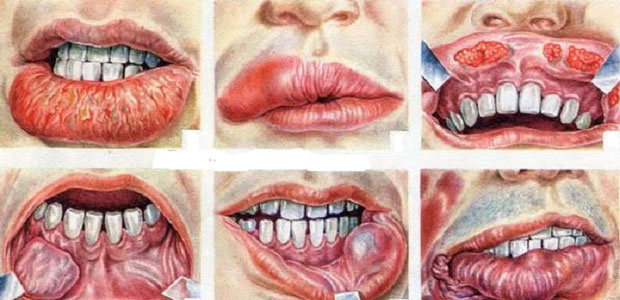
What are the symptoms of oral cancer?
Treatment methods for oral cancer
What is the postoperative care of oral cancer?
Provide liquid diet to the patient after surgery and change into semi-liquid diet about one week after the operation.
Observe the color, temperature and elasticity of the patient’s skin flap, if it is low in temperature, greenish purple and increasingly aggravates, turn to the doctor instantly.
Aspirate the patient’s secretions in the mouth, nasal cavity and pharynx to keep the airway unobstructed.
If the patient is not able to talk, check whether there are symptoms of airway obstruction, such as fidget and nasal flaring, if any, inform the doctor.
 viber
viber