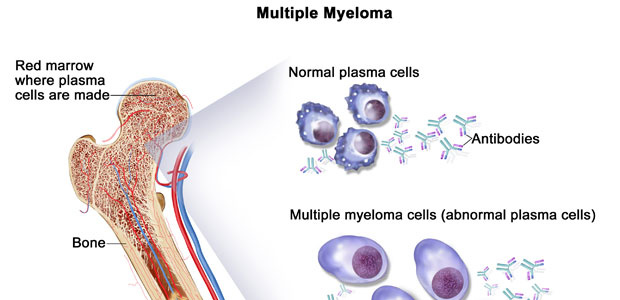
What is Multiple Myeloma?
Multiple myeloma refers to a malignant tumor in hematological system, originating from plasma cells (a type of white blood cell generated in the bone marrow). Normal plasma cell is responsible for producing antibodies which can fight against infection, while malignant plasma cell---- myeloma cell proliferates in great numbers in the bone marrow, resulting in disorder of patients’ life, caused symptoms such as anemia, bone pain, fracture, decreased immunity, hypercalcemia, proteinuria, renal inadequacy, etc.
What is the incidence of multiple myeloma?
Every year, there are about two out of ten thousand people diagnosed with multiple myeloma which is believed to be the second common malignant tumors arising from blood. It is more commonly seen in the elderly and 50-65 years old is the high incidence age, but age of onset trends to be younger in recent years. Men have higher incidence of multiple myeloma than women, and the ratio is 1.6:1. With age increasing, the incidence of multiple myeloma can also rise, which has brought more and more harm to people’s lives and lowered their quality of life, thus multiple myeloma has become a malignant hematological tumor that people cannot neglect. Besides, the occurrence of multiple myeloma has certain relation to race, which indicates that the incidence for black people is slightly higher.
What are the causes of multiple myeloma?
It is still not clear what cause multiple myeloma, but it may be related to ionizing radiation, chronic antigenic stimulation, herpes virus infections associated with EB virus or Kaposi's sarcoma. In addition, it may also be associated with a number of cell factors, for example IL-6 which is the growth factor of multiple myeloma.
What are the symptoms of multiple myeloma?
What are the diagnostic methods of multiple myeloma?
Treatment methods for multiple myeloma
Family nursing for patient with multiple myeloma
Rest: patients can do appropriate activities, but never do strenuous exercise, preventing falls and bruise.
Bed:in order to prevent pathologic fracture, patient should sleep on the hard bed instead of elastic and soft bed.
Diet: food should be high in protein, rich in vitamins and digestible. Patients with renal dysfunction should be given low sodium, low protein diet, in order to reduce the burden on the kidneys. If hyperuricemia and hypercalcemia occur, patients should be encouraged to drink more water and daily urinary volume should be maintained above 2000ml, so as to alleviate their clinical symptoms.
Mental guide: giving patients more love and care, helping them face up to the reality, alleviating their anxieties, encouraging them to face their conditions positively.
 viber
viber