Due to its wide coverage and strong lethality, pancreatic cancer is of great harm to people. Experts point out that early diagnosis of pancreatic cancer is an important factor in determining the treatment effect. Therefore, it is necessary for us to learn about related pancreatic cancer diagnosis methods.
Diagnostic Methods of Pancreatic Cancer?
1. Ultrasound examination: Abdomen ultrasound is the preferred method for pancreatic cancer detection and diagnosis. It is easy to operate, harmless, non-radioactive and observable from multi-axial planes. Moreover, it can well reveal the internal structure of the pancreas and whether there is obstruction in the biliary tract, if any, site of the obstruction. On the other hand, it has the limitation of small field of vision and being easy to be affected by bodybuild and the gas within stomach and intestinal tract. In addition, it relies much on the operating doctor’s professional level, experience and notion, as well as the equipments. It is to a certain degree subjective, thus needs to be comprehensively considered whether to be combined with CT, MRI and laboratory examination.
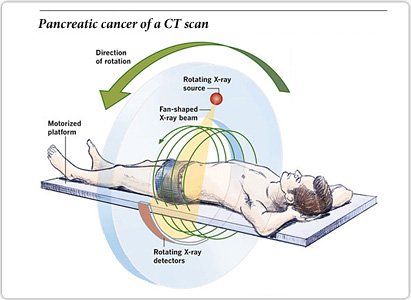
2. CT: So far, CT is the best non-invasive imaging examination method for pancreatic cancer detection. It is mainly used in pancreatic cancer diagnosis and staging. Plain scanning can reveal the size and site of the lesion, but cannot accurately diagnose, nor can it help reveal its relation with surrounding structures. Strengthened scan can better reveal the size, site, shape, internal structure and their relation with surrounding construction. CT scans can more accurately determine whether there are liver transfusion and swollen lymph nodes.
CT scan is one of the increasingly widely used cancer examination methods in recent years. It can more accurately determine the texture and range of the cancer and has high value in cancer staging and treatment determination.
3. Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) and Magnetic Resonance Cholangiopancreatography (MRCP): so far they are not recommended as the preferred methods for pancreatic cancer diagnosis. However, if the patient is allergic to contrast agent used to enhance the effect of CT scan, MRI can be used to replace CT in diagnosing and staging cancer clinically. Moreover, for those pathological changes whose characteristics are difficult to determine, MRI can be used on the basis of the CT examination to complement the shortcomings of CT imaging. MRCP has prominent advantage in determining whether there is obstruction in the biliary tract, if any, the site and reason of the obstruction. Compared with endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) and Percutaneous Transhepatic Cholangiography (PTC), which are invasive, MRCP is safer.
 viber
viber