- Basic
- Symptoms
- Diagnosis
- Treatments
What Is Liver Cancer?
Liver cancer refers to malignant tumor occurred in liver, which includes primary liver cancer and transferred liver cancer. Primary liver cancer is one of the most commonly seen malignant tumor in clinical. According to the newest statistics, there are about 600,000 liver cancer patients appear each year, and the incidence rate of liver cancer ranks the sixth while its mortality ranks the third among all kinds of cancers.
Some East Asian countries or Southest Asian countries or regions like Vietnam, the Philippines, Malaysia, Singapore are highly risky areas for liver cancer. Among liver cancer patients, aged people account for the most, and usually age 50-60 are the highly risky ages. Generally speaking, male liver cancer patients are 7-10 times the amount of female patients. To one’s fortunate, development of medical technologies has provided more and more effective methods for liver cancer treatments and also brought new hope for liver cancer patients.
Causes of Liver Cancer
By now, we still don’t know what exactly have directly caused liver cancer, but the following factors are definitely related to liver cancer:
1. Chronic hepatitis: viral hepatitis is somehow concerned with liver cancer. Certain statistics show that more than 30% liver cancer patients have the history of chronic hepatitis, especially type B hepatitis is most common;
2. Cirrhosis: medical observation found that there are 50-90% liver cancer patients have different degree of cirrhosis, therefore, cirrhosis patients shall actively cooperate treatment and go to hospital for periodically check-up to prevent the occurrence of liver cancer;
3. Long term drink polluted water;
4. Long term eat milden and rot food;
5. Long term take salted, fried or baked food;
Besides these, parasitic diseases (mainly referring to liver fluke), long-term alcohol drinking as well as environment pollution are also the causes of liver cancer.
Staging of Liver Cancer
The principles for staging liver cancer have not reached to an agreement in international society, for example, U.S.A adopt TNM staging standards in which T stands for the sizes of tumor, N for metastasis situation, M for whether cancer cells have transferred to other organ, while for the detailed subdivisions in the T, N, M, see details in the followings:
T1 means that the diameter of tumor is below 2cm, without blood or lymph metastasis;
T2 means that although the diameter of tumor is below 2cm, while tumor has invaded to adjacent blood vessel; or there are two cancer lumps whose diameters are below 2cm, and no invasion has occurred to blood vessel; or the diameter of tumor is 2cm or above, but no invasion has occurred to blood vessel.
T3 means that the diameter of tumor has reached to 2cm or above and the tumor has invaded to blood vessels; or there are several lumps whose diameters have not reached 2 cm, but these lumps have invaded into blood vessels; or there are one or more tumors whose diameter have exceeded 2cm.
T4 means that both lobes of liver have got tumors or tumor has invaded to portal vein of liver;
N0 means that no lymph node metastasis has occurred, while N1 means that lymph node metastasis has occurred ;
M0 means that no distant metastasis has occurred, while M1 means that the contrary.
Stage I: T1N0M0 patients belong to Stage I, and are early stage patients;
Stage II: T2N0M0 patients belong to Stage II;
Stage III: T1N1M0, T2N1M0, T3N1MO patients belong to Stage III;
Stage IVa: T4M0 patients have not occurred distant metastasis;
Stage IVb: T4M1 patients have occurred distant metastasis.

At early stage, symptoms of liver cancer are not obvious. Mostly, symptoms can be detected at an advanced stage. In daily life, many patients ignore early symptoms and they are told that they are advance level cancer patients when they realize. Then what are symptoms of liver cancer?
1. Hepatalgia: Continuous dull pain in hepatic region of right upper quadrant is an important and the most frequent symptom of primary hepatic carcinoma. It is caused by rapidly increasing liver which make liver capsule tense or by malignant tumors’ violation of liver capsule or peritoneum. It can be continuous dull pain or gas pain. When malignant tumors violate diaphragma, patient will feel pain in right shoulder or right back. Tumors growing toward rear right can cause pain in right waist. When cancer nodules rupture, necrotic cancer tissues and blood flow into abdomen. Then patient suffers severe abdominal pain. Symptoms and signs of peritonitis appear.
2. Hepatomegaly: It is the most frequent sign of primary liver cancer. Liver is increasing swelling, solid with uneven surface. Different-size tubercles or lumps cause local eminence, untidily borderline with tenderness.
3. Jaundice: One third of patients suffer it. Mostly, it occurs at an advanced stage liver cancer. And it is caused by damage of liver cells or by malignant tumors which press bile duct.
4. Fever: In general, patient suffers low-grade fever, occasionally above 39℃. It can be continuous low-grade fever or irregular hyperpyrexia. The reason is that organism absorbs a large quantity of damaged tumor tissues. Or it may be result of cholangitis or concurrent infection caused by malignant tumors pressing bile duct.
5. Alimentary canal and general symptoms: Decreased food appetite, dyspepsia, nausea, emesia, diarrhea, acratia, maciei, asthenia universalis and cachexia.
6. Symptoms of metastasis: Relative symptoms appear when liver cancer with metastasis to stomach, bone, pelvis cavity and brain. For example, pulmonary metastasis cause cough and emptysis; pleural metastasis cause chest pain and bloody hydrothorax; osseous metastasis cause local pain or pathologic fracture; metastasis to spinal column or press spinal nerves can cause local pain and paraplegia; Brain metastasis can cause headache, emesis and signs of nerve localization.
7. Other symptoms: Endocrine syndrome or metabolic endocrine, also called syndrome associated with cancer, are caused by abnormal metabolism in malignant tumors.
(1) Spontaneous hypoglycemia: 10% to 30% of patients suffer it. It is caused by liver cells secreting insulin or insulin-like substance not only in pancreatic islet. It is also caused by hepatocellular carcinoma tissue consuming too much glucose. Sever patients may hepatocyte, shock even die.
(2) Globulism: 2% to 10% patients suffer it. It is caused by increasing haemopoietin in circulation.
(3) Others: There are also hyperlipemia, hypercalcinemia, carcinoid syndrome, gonadotrophins syndrome, skin porphyria and dysfibrinogenemia. These symptoms may be related to synthesis of paraprotein, dystopia endocrine seretion and porphyrin metabolism disorder in liver cancer tissue.
Liver cancer refers to malignant tumor in liver, with patients’ average age 44. The average live time is half a year without timely treatment or proper treatment plan. There is no obvious symptom in the early stage. Once detected, it’s already in middle or advanced stage. Therefore, it’s very important to make a timely and effective diagnosis for liver cancer.
1. Ultrasound diagnosis: It applies B-type ultrasonography to indicate the sizes, shape of tumor and can discover the lesion whose diameter is about 2cm or even less, and it has became the most common and effective method for diagnosing liver cancer;
2. Radioisotopic hepatic scanning: shows enlargement of liver and liver has lost its normal morph. But such scanning can hardly indicate the tumor with diameter less than 3 cm on the films;
3. CT check: CT features high resolution and can detect early liver cancer with tumor’s diameter even being about 1cm;
4. MRI: MRI has high sensitive and can distinguish benign and malignant tumor;
5. Selective celiac or hepatic arteriography: it can indicate out tumor with the diameter even among 0.5-1cm and localize the position of lesion, as well as its sizes, distributions. This is especially valid for small tumor localization of liver cancer.
Experts from Modern Cancer Hospital Guangzhou remind that as for liver cancer’s diagnosis, in order to guarantee the effect and safety of exam, it’s necessary to go to a regular hospital.
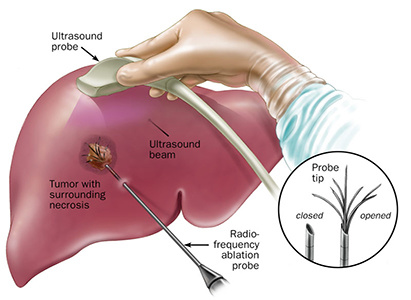
Radiofrequency Ablation
Liver cancer is a malignant cancer that severely threatens people’s health and all along has a high death rate. Failure to treat liver cancer in its early stage can probably lead to death. There are many different liver cancer treatments, which are of different effects. Therefore, the choice of treatment is very important.
Common Treatment for Liver Cancer
For most liver cancer patients, the most common treatments are surgery and traditional chemotherapy. Generally speaking, most liver cancer patients may have symptoms of cancer diffusion and transfusion. Moreover, their general symptoms are severer and physical constitutions are relatively poorer. Only 13% of advanced liver cancer patients have the chance of undergoing surgery, after which their life quality is comparatively poorer. Therefore, surgery and traditional chemotherapy is not recommended in advanced liver cancer treatment.
The Best Treatment for Advanced Liver Cancer
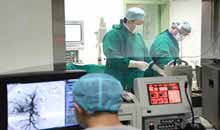
Nowadays, interventional therapy is widely used in liver cancer treatment. It is a method to diagnose and treat cancer by inserting a specially-made puncture needle or duct into the tumor area of the liver under the guidance of MRI, CT and B-ultrasound. It mainly includes liver artery chemotherapy embolism, which has good effect and is the best treatment method for advanced liver cancer.
Besides interventional therapy and surgery, combined therapy of TCM and Western medicine is also alternative treatment for liver cancer. For advanced liver cancer patients, single treatment of radiation therapy or chemotherapy can not gain ideal treatment effect. What’s more, they can bring to patients great side-effect and painfulness. However, Chinese medicine can not only ease patient’s discomfort, but also reduce the side-effect of chemotherapy. Clinically, treatment for advanced liver cancer is usually composed of Chinese medicine, which is used as a leading treatment, and Western treatment of radiation and chemotherapy, which are used as a supplementary treatment. Together they effectively improve the patient’s life quality.
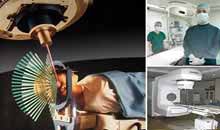
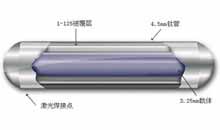
Radiofrequency Ablation
It is an image-guided technique that heats and destroys liver tumor. Under the guidance of image, radiofrequency ablation, a physical method to inactive and kill the liver tumor, is performed with minimally invasive paracentesis to introduce the heat generator into the liver tumor. Ablation is targeting and can affect the liver tumor strongly while no side effect happens to normal tissues around. The result of radiofrequency ablation is same as invasive surgery with the advantages of smaller trauma, fewer side effects and quicker recovery.
In summary, there are many treatment methods for liver cancer and it is very important to choose the proper treatment method. Experts from Modern Cancer Hospital Guangzhou remind that whatever choice is made, interventional therapy or surgery, to get better treatment effect, liver cancer patients should go to regular hospitals for the treatment.
If you have any questions, please contact us via online consultation, email or phone call. If you find our website useful, please follow our FaceBook and YouTube, health information will be updated regularly.