In our daily life, many women may occur to abdominal pain and abdominal distension, which is believed to be cause by indigestion. However, if it is not improved or cured after a period of treatments (generally two weeks to one month), or it is recurrent frequently, one should be vigilant and take further tests. Since this could be a warning signal of ovarian cancer.
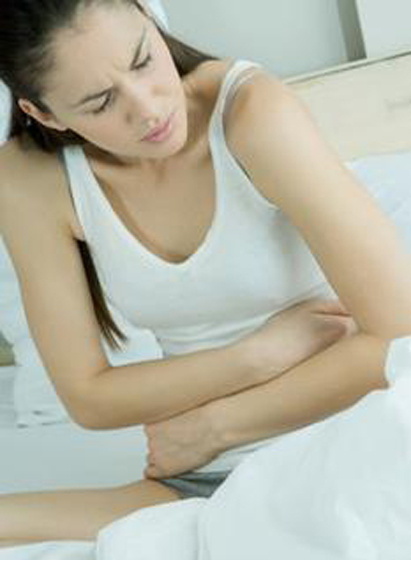

Many people may be confused why ovarian cancer is related to abdominal bloating and abdominal pain or other gastrointestinal symptoms. Experts from Modern Cancer Hospital Guangzhou will explain you the details below: these symptoms appear when the tumors in the patient’s abdomen oppresses or adheres to the surrounding ligaments, or when the ascites continuously stimulating to the involved organs.
Currently, the exactly etiology of ovarian cancer is not certified clearly yet. However, epidemiological studies have shown that women who don’t have a baby or who have their first baby in the middle age (more than 35 years) are in a higher risk for ovarian cancer. On the contrary, the young primiparous & pregnant mothers or those who do breastfeeding have a smaller risk, which may be decreased by 30 % -60%.
It is reported that the specific risk factors for ovarian cancer include: a family history of ovarian cancer or breast cancer, age, high fat diet, sterility etc. For ovarian masses during one’s menarche or postmenopausal, tumor should be considered. Besides, women who have the following conditions should be always on guard against the pathological changes of their ovaries: irregular menstruation, adnexal masses, and gynecological diseases.
Experts from Modern Cancer Hospital Guangzhou recommend that women who have abdominal pain & bloating or any related recurrent symptoms should visit a doctor for gynecological examination and ovarian cancer assessment. Women during the reproductive age should pay attention to their own health and take annual medical examination periodically. As for those who have ovarian cancer risk factors, a semi-annual gynecological examination and type B ultrasonic examination should be conducted.
Common screening methods for ovarian diseases are gynecological examinations and ultrasonography. While for some lesions that are difficult to refer or have been clearly confirmed, further tests like CT scan, MRI, PET / CT, biopsy or other lab tests should be conducted.
If you have any questions, please contact us via online consultation, email or phone call. If you find our website useful, please follow our FaceBook and YouTube, health information will be updated regularly.