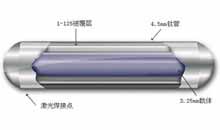
What is PDT (Photodynamic Therapy)?
Photodynamic therapy (PDT) is a treatment that uses a drug, called a photosensitizer or photosensitizing agent, and a particular type of light. When photosensitizers are exposed to a specific wavelength of light, they produce a form of oxygen that kills nearby cells.PDT was approved by the U.S. FDA for clinical application in 1996 and approved for clinical application by Chinese SFDA in 2003.
How is PDT used to treat cancer?

In the first step of PDT for cancer treatment, a photosensitizing agent is injected into the bloodstream. The agent is absorbed by cells all over the body but stays in cancer cells longer than it does in normal cells. Approximately 24 to 72 hours after injection, the tumor is exposed to light when most of the agent has disappeared from normal cells but remains in cancer cells. The photosensitizer in the tumor absorbs the light and produces an active form of oxygen that can destroy nearby cancer cells.
In addition to directly killing cancer cells, PDT appears to shrink or destroy tumors in two other ways. The photosensitizer can damage blood vessels in the tumor, thereby preventing the cancer from receiving necessary nutrients. PDT also may activate the immune system to attack the tumor cells.
The light used for PDT can come from a laser or other sources. Laser light can be directed through fiber optic cables (thin fibers that transmit light) to deliver light to areas inside the body. For example, a fiber optic cable can be inserted through an endoscope (a thin, lighted tube used to look at tissues inside the body) into the lungs or esophagus to treat cancer in these organs. Light-emitting diodes (LEDs), other light source, may be used for surface tumors, such as skin cancer.
What are the advantages of PDT?
Minimally invasive: avoid surgery and wound. Less pain caused.Quick effects: the effects show up in 48 to 72 hours.To prevent cancer recurrence: destroy tiny lesions and minimize tumor recurrence.Few complications: has low toxicity. It well suits patients with advanced cancer or elderly patients and those with poor physical status.
Does PDT have any complications or side effects?
 Porfimer sodium makes the skin and eyes sensitive to light for approximately 6 weeks after treatment. Thus, patients are advised to avoid direct sunlight and bright indoor light for at least 6 weeks.
Porfimer sodium makes the skin and eyes sensitive to light for approximately 6 weeks after treatment. Thus, patients are advised to avoid direct sunlight and bright indoor light for at least 6 weeks.
Photosensitizers tend to build up in tumors and the activating light is focused on the tumor. As a result, damage to healthy tissue is minimal. However, PDT can cause burns, swelling, pain, and scarring in nearby healthy tissue.
Other side effects of PDT are related to the area that is treated. They can include coughing, trouble swallowing, stomach pain, painful breathing, or shortness of breath; these side effects are usually temporary.
What types of cancer are currently treated with PDT?

- Oropharyngeal cancereffective rate reaches 75% -100% for early oral cancer and nasopharyngeal cancer.
- Esophageal cancer can remarkably improve obstruction of progressive esophageal cancer; also take effect in cervical esophageal cancer and disseminated submucosal esophageal cancer; be capable of eliminating intracavity tumor from esophageal cancer treated with stent placement.
- Barrett’s esophagus not only can eliminate Barrett’s esophagus epithelium, but also can treat early esophageal adenocarcinoma.
- Lung cancer survival rate for early bronchial cancer reaches 90%. Improvement rate for progressive obstructive bronchial carcinoma reaches 85%.
- Gastric cancer survival rate for early gastric cancer is 85%; effective in improving symptoms of progressive gastric cancer.
- Bladder Cancer to treat carcinoma in situ. Effective rate for progressive cancer reaches 71%.
- Other cancers colorectal cancer, carcinoma of bile duct (especially hilar cholangiocarcinoma), pancreatic, ampullary cancer, abdominal cancer, pleura mesothelioma and abdominal mesothelioma, liver cancer, brain tumor and genitourinary tract cancer.
Recommended Links
SUSAN: Interventional Therapy and Biological Immunotherapy Defeat Cancer Recurrence Successfully
MIMIE: Modern Cancer Hospital Guangzhou Gave Me a Second Life
Aida Nuguid: Modern Cancer Hospital Guangzhou Is the Instrument that God Sent to Me